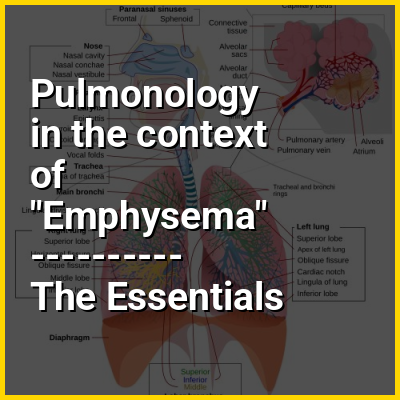
Pulmonology (/ˌpʌlməˈnɒlədʒi/, /ˌpʊlməˈnɒlədʒi/, from Latin pulmō, -ōnis "lung" and the Greek suffix -λογία -logía "study of"), pneumology (/nʊˈmɒlədʒi, njʊ-/, built on Greek πνεύμων pneúmōn "lung") or pneumonology (/nʊmənˈɒlədʒi, njʊ-/) is a medical specialty that deals with diseases involving the respiratory tract. It is also known as respirology, respiratory medicine, or chest medicine in some countries and areas.
Pulmonology is considered a branch of internal medicine, and is related to intensive care medicine. Pulmonology often involves managing patients who need life support and mechanical ventilation. Pulmonologists are specially trained in diseases and conditions of the chest, particularly pneumonia, asthma, tuberculosis, emphysema, and complicated chest infections.