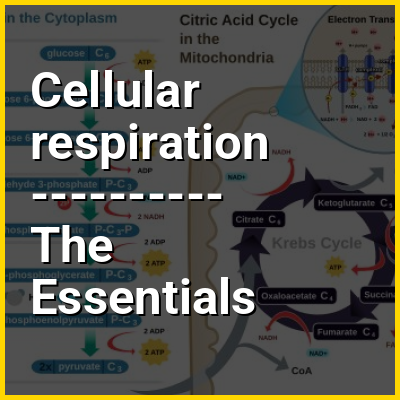
Cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing biological fuels using an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which stores chemical energy in a biologically accessible form. Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells to transfer chemical energy from nutrients to ATP, with the flow of electrons to an electron acceptor, and then release waste products.
If the electron acceptor is oxygen, the process is more specifically known as aerobic cellular respiration. If the electron acceptor is a molecule other than oxygen, this is anaerobic cellular respiration – not to be confused with fermentation, which is also an anaerobic process, but it is not respiration, as no external electron acceptor is involved.