Materials covered in this trivia questions quiz
Study Hint 1
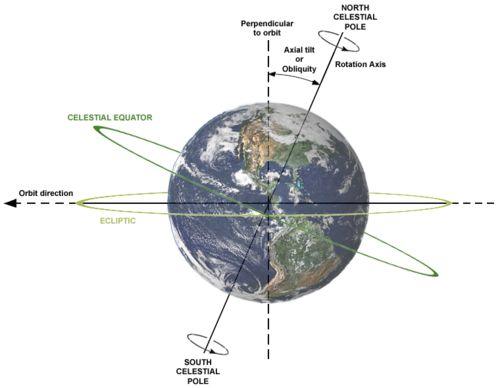
Question: In the context of the Ptolemaic system, what was the primary function of the celestial pole?
Trivia Question Study Fact: Within the Ptolemaic system, a geocentric model of the universe, the apparent daily rotation of the stars was explained by positing they were fixed upon a celestial sphere rotating around an axis passing through Earth's geographical poles. This axis, crucial to understanding the observed stellar movement, is referred to as the celestial pole.
Trivia Question Explanation: The Ptolemaic system explained the daily movement of stars by proposing they were affixed to a rotating celestial sphere, with the celestial pole defining the axis of this rotation relative to Earth’s geographical poles.
Return to Question
Study Hint 2
Question: In the context of diurnal motion, the apparent paths traced by stars across the sky are specifically defined by movement around what key points?
Trivia Question Study Fact: Diurnal motion, the apparent daily movement of celestial objects, occurs around Earth's celestial poles due to the planet's rotation on its axis. This rotation causes stars to trace circular paths, known as diurnal circles, across the sky over a period of roughly 24 hours.
Trivia Question Explanation: The diurnal motion of stars is defined as their apparent movement around the two celestial poles, which are projections of Earth’s rotational axis into space, completing a full circle in approximately one day.
Return to Question
Study Hint 3
Question: In the context of celestial mechanics, the apparent fixed positions of the celestial poles are ultimately an illusion because of what long-term phenomenon?
Trivia Question Study Fact: The celestial poles are defined as the points where Earth's rotational axis, when extended into space, intersects the celestial sphere. These poles aren't static; they slowly trace circles in the sky over approximately 25,700 years due to the precession of the equinoxes, and are further affected by nutation, polar motion, axial tilt, and the proper motions of stars. Therefore, defining them requires specifying a particular epoch, like J2000.0, to account for these movements.
Trivia Question Explanation: The precession of the equinoxes causes the celestial poles to trace out circles on the celestial sphere over a period of about 25,700 years, meaning their positions gradually shift against the background of stars.
Return to Question
Study Hint 4
Question: In the context of geocentrism, the perceived daily movement of stars across the sky was attributed to the rotation of what structure around Earth?
Trivia Question Study Fact: Within the geocentric model, the apparent daily rotation of stars was explained by their being fixed on a celestial sphere that revolved around Earth once a day, with this sphere rotating around an axis extending through Earth's geographical poles and a corresponding celestial pole.
Trivia Question Explanation: Geocentric models posited that stars were embedded in a celestial sphere that rotated around a fixed Earth, with the sphere’s axis of rotation aligned with Earth’s geographical poles and a corresponding celestial pole, creating the illusion of stellar movement.
Return to Question
Study Hint 5
Question: In the context of the geocentric model, the perceived daily movement of stars across the sky was attributed to the rotation of what?
Trivia Question Study Fact: Within the geocentric model, the apparent daily rotation of stars was explained by their being fixed on a celestial sphere that revolved around Earth once a day, with this sphere rotating around an axis extending from the geographical poles of Earth and defining the location of the celestial pole.
Trivia Question Explanation: Geocentric models posited that stars were embedded in a celestial sphere that rotated around a fixed Earth, with the axis of this sphere aligned with Earth’s geographical poles, thus explaining the observed daily motion of the stars.
Return to Question
Study Hint 6
Question: In the context of Geocentrism, the Celestial pole is considered…
Trivia Question Study Fact: Within geocentric models like those proposed by Aristotle and Ptolemy, the stars were not considered to orbit Earth directly, but rather to be fixed on a celestial sphere that rotated around Earth once daily, with its axis extending through Earth's geographical poles and a corresponding celestial pole.
Trivia Question Explanation: Geocentric models posited a celestial sphere containing the stars, and this sphere was believed to rotate around a fixed Earth, pivoting on an axis that aligned with Earth’s geographical poles and a corresponding celestial pole.
Return to Question
Study Hint 7
Question: In the context of Poles_of_astronomical_bodies, a Celestial_pole is considered…
Trivia Question Study Fact: The celestial poles serve as fundamental reference points for defining the poles of astronomical bodies like planets, stars, and comets. These poles are determined by the body's axis of rotation relative to the celestial sphere, effectively projecting an imaginary axis through the body and extending to these celestial reference points.
Trivia Question Explanation: An astronomical body's poles are defined by its axis of rotation and its relationship to the celestial sphere, meaning the poles are the points where that axis extends to intersect the celestial sphere.
Return to Question
Study Hint 8
Question: In the context of pole stars, the celestial poles are defined by their relationship to what fundamental characteristic of an astronomical body?
Trivia Question Study Fact: A pole star's significance stems from its apparent alignment with an astronomical body's axis of rotation; for observers at either the North or South Pole, a true pole star would appear directly overhead, marking the celestial pole.
Trivia Question Explanation: Pole stars are defined by their close alignment with the axis of rotation of the astronomical body they are observed from, making them useful for determining the position of the celestial poles.
Return to Question
Study Hint 9
Question: In the context of circumpolar stars, the size of the circumpolar circle, which defines the area of continuously visible stars, is primarily determined by…
Trivia Question Study Fact: Circumpolar stars maintain visibility throughout the night, and potentially the day, because their apparent location near a celestial pole results in them never setting below the horizon for observers at specific latitudes. The size of the area in the sky containing these stars, known as the circumpolar circle, is directly related to the observer's latitude – the closer to a pole, the larger the circle.
Trivia Question Explanation: The angular radius of the circumpolar circle is equivalent to the observer’s latitude, meaning that locations closer to either pole will have a larger area of sky containing stars that never set.
Return to Question
Study Hint 10
Question: In the context of Wufang Shangdi, the celestial pole is considered to be intrinsically linked to…
Trivia Question Study Fact: Within the framework of Wufang Shangdi theology, the five deities are understood as manifestations of the supreme God of Heaven, and their cosmic activity is represented by constellations rotating around the celestial pole, mirroring the order visible in the starry vault. These deities aren't separate gods, but rather different aspects or 'faces' of the singular divine power.
Trivia Question Explanation: The Wufang Shangdi theology describes the five deities as representing Heaven’s cosmic activity, which is visibly mirrored in the constellations rotating around the celestial pole, effectively making the pole a central point of their manifestation.
Return to Question