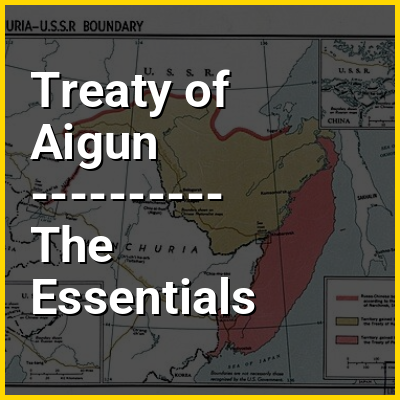
The Treaty of Aigun was an 1858 treaty between the Russian Empire and Yishan, official of the Qing dynasty of China. It established much of the modern border between the Russian Far East and China by ceding much of Manchuria (the ancestral homeland of the Manchu people), now known as Northeast China. Negotiations began after China was threatened with war on a second front by Governor-General of the Far East Nikolay Muraviev when China was suppressing the Taiping Rebellion. It reversed the Treaty of Nerchinsk (1689) by transferring the land between the Stanovoy Range and the Amur River from the Qing dynasty to the Russian Empire. Russia received over 600,000 square kilometers (231,660 sq mi) of what became known as Outer Manchuria. While the Qing government initially refused to recognize the validity of the treaty, the Russian gains under the Treaty of Aigun were affirmed as part of the 1860 Sino-Russian Convention of Peking.
>>>PUT SHARE BUTTONS HERE<<<
👉 Treaty of Aigun in the context of Treaty of Nerchinsk
The Treaty of Nerchinsk of 1689 was the first treaty between the Tsardom of Russia and the Qing dynasty of China after the defeat of Russia by Qing China at the Siege of Albazin in 1686. The Russians gave up the area north of the Amur River as far as the Stanovoy Range and kept the area between the Argun River and Lake Baikal. This border along the Argun River and Stanovoy Range lasted until the Amur Annexation via the Treaty of Aigun in 1858 and the Convention of Peking in 1860. It opened markets for Russian goods in China, and gave Russians access to Chinese supplies and luxuries.
The agreement was signed in Nerchinsk on 27 August 1689. The signatories were Songgotu on behalf of the Kangxi Emperor and Fyodor Golovin on behalf of the Russian tsars Peter I and Ivan V.
- ⭐ Core Definition: Treaty of Aigun
- 👉 Treaty of Aigun in the context of Treaty of Nerchinsk
- Treaty of Aigun in the context of Outer Manchuria
- Treaty of Aigun in the context of Vladivostok
- Treaty of Aigun in the context of Amur Annexation
- Treaty of Aigun in the context of Ainu people
- Treaty of Aigun in the context of Xianfeng Emperor
- Treaty of Aigun in the context of Yishan (official)
Treaty of Aigun in the context of Outer Manchuria
Outer Manchuria, sometimes called Russian Manchuria, refers to a region in Northeast Asia that is now part of the Russian Far East but historically formed part of Manchuria (until the mid-19th century). While Manchuria now more normatively refers to Northeast China, it originally included areas consisting of Priamurye between the left bank of Amur River and the Stanovoy Range to the north, and Primorskaya which covered the area in the right bank of both Ussuri River and the lower Amur River to the Pacific Coast. The region was ruled by a series of Chinese dynasties and the Mongol Empire, but control of the area was ceded to the Russian Empire by Qing China during the Amur Annexation in the 1858 Treaty of Aigun and 1860 Treaty of Peking, with the terms "Outer Manchuria" and "Russian Manchuria" arising after the Russian annexation.
Prior to its annexation by Russia, Outer Manchuria was predominantly inhabited by various Tungusic peoples who were categorized by the Han Chinese as "Wild Jurchens". The Evenks, who speak a closely related Tungusic language to Manchu, make up a significant part of the indigenous population today. When the region was a part of the Qing dynasty, a small population of Han Chinese men migrated to Outer Manchuria and married the local Tungusic women. Their mixed descendants would emerge as a distinct ethnic group known as the Taz people.
Treaty of Aigun in the context of Vladivostok
Vladivostok (/ˌvlædɪˈvɒstɒk/ VLAD-iv-OST-ok; Russian: Владивосток, lit. '"Ruler of the East"', IPA: [vlədʲɪvɐˈstok] ) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai and the capital of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia. It is located around the Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, covering an area of 331.16 square kilometers (127.86 square miles), with a population of 603,519 residents as of 2021. Vladivostok is the second-largest city in the Far Eastern Federal District, as well as the Russian Far East, after Khabarovsk. It is located approximately 45 kilometers (28 mi) from the China–Russia border and 134 kilometers (83 mi) from the North Korea–Russia border.
Vladivostok was historically part of Outer Manchuria. Shortly after the signing of the Treaty of Aigun between Qing China and the Russian Empire and affirmed by the Convention of Peking – from which it is also known as the Amur Annexation – the city was founded as a Russian military outpost on July 2, 1860. In 1872, the main Russian naval base on the Pacific Ocean was transferred to the city, stimulating its growth. In 1914 the city experienced rapid growth economically and ethnically diverse with population exceeding over 100,000 inhabitants with slightly less than half of the population being Russians. During this time, large Asian communities developed in the city. The public life of the city flourished; many public associations were created, from charities to hobby groups. After the outbreak of the Russian Revolution in 1917, Vladivostok was occupied in 1918 by White Russian and Allied forces, the last of whom, from the Japanese Empire, were not withdrawn until 1922 as part of its wider intervention in Siberia; by that time the antirevolutionary White Army forces had collapsed. That same year, the Red Army occupied the city, absorbing the Far Eastern Republic into the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic. Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, the city became a part of the Russian Federation.
Treaty of Aigun in the context of Amur Annexation
Between 1858 and 1860, the Russian Empire annexed territories adjoining the Amur River belonging to the Chinese Qing dynasty through the imposition of unequal treaties. The 1858 Treaty of Aigun, signed by the general Nikolay Muravyov representing the Russian Empire and the official Yishan representing Qing China, ceded Priamurye—a territory stretching from the Amur River north to the Stanovoy Mountains, but the Qing government initially refused to recognize the treaty's validity. Two years later, the Second Opium War concluded with the Convention of Peking, which affirmed the previous treaty as well as an additional cession including the entire Pacific coast to the Korean border, as well as the island of Sakhalin to Russia. These two territories roughly correspond to modern-day Amur Oblast and Primorsky Krai, respectively. Collectively, they are often referred to as Outer Manchuria, part of the greater region of Manchuria.
Treaty of Aigun in the context of Ainu people
The Ainu are an indigenous ethnic group who reside in northern Japan and southeastern Russia, including Hokkaido and the Tōhoku region of Honshu, as well as the land surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, such as Sakhalin, the Kuril Islands, the Kamchatka Peninsula, and the Khabarovsk Krai. They have occupied these areas, known to them as "Ainu Mosir" (Ainu: アイヌモシㇼ, lit. 'the land of the Ainu'), since before the arrival of the modern Yamato and Russians. These regions are often referred to as Ezochi (蝦夷地) and its inhabitants as Emishi (蝦夷) in historical Japanese texts. Along with the Yamato and Ryukyuan ethnic groups, the Ainu people are one of the primary historic ethnic groups of Japan and are along with the Ryukyuans and Bonin Islanders one of the few ethnic minorities native to the Japanese archipelago.
Official surveys of the known Ainu population in Hokkaido received 11,450 responses in 2023, and the Ainu population in Russia was estimated at 300 in 2021. Unofficial estimates in 2002 placed the total population in Japan at 200,000 or higher, as the near-total assimilation of the Ainu into Japanese society has resulted in many individuals of Ainu descent having no knowledge of their ancestry.
Treaty of Aigun in the context of Xianfeng Emperor
The Xianfeng Emperor (17 July 1831 – 22 August 1861), also known by his temple name Emperor Wenzong of Qing, personal name Yizhu, was the eighth emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the seventh Qing emperor to rule over China proper. During his reign, the Qing dynasty experienced several wars and rebellions including the Taiping Rebellion, the Nian Rebellion, and the Second Opium War. He was the last Chinese emperor to exercise sole power.
The fourth son of the Daoguang Emperor, he assumed the throne in 1850 and inherited an empire in crisis. A few months after his ascension, the Taiping Rebellion broke out in southern China and rapidly spread, culminating in the fall of Nanjing in 1853. Contemporaneously, the Nian Rebellion began in the north, followed by ethnic uprisings (the Miao Rebellion and the Panthay Rebellion) in the south. The revolts ravaged large parts of the country, caused millions of deaths and would not be quelled until well into the reign of the Xianfeng Emperor's successor. Qing defeat during the first phase of the Second Opium War led to the Treaty of Tientsin and the Treaty of Aigun, the latter of which resulted in the cession of much of Manchuria to the Russian Empire. Negotiations broke down and hostilities resumed soon after, and in 1860 Anglo-French forces entered Beijing and burned the Old Summer Palace. The Xianfeng Emperor was forced to flee for the imperial estate at Jehol, and the Convention of Peking was negotiated in his absence.
Treaty of Aigun in the context of Yishan (official)
Yishan (Manchu: ![]() I Šan; 13 June 1790 – 30 June 1878), courtesy name Jingxuan, was a Manchu lesser noble and official of the Qing dynasty. He is best known for his failure to defend Guangzhou (Canton) from British forces during the First Opium War, and for signing the treaties of Kulja and Aigun with the Russian Empire in 1851 and 1858 respectively.
I Šan; 13 June 1790 – 30 June 1878), courtesy name Jingxuan, was a Manchu lesser noble and official of the Qing dynasty. He is best known for his failure to defend Guangzhou (Canton) from British forces during the First Opium War, and for signing the treaties of Kulja and Aigun with the Russian Empire in 1851 and 1858 respectively.
Yishan was born in Beijing or Mukden (modern-day Shenyang), Qing Dynasty, on 13 June 1790. Being a distant relative of the Qing Dynasty Royal Family, he entered the Qing bureaucracy without taking the Imperial examination at the age of 20, in 1810. In 1821, after the Daoguang Emperor inherited the throne from the Jiaqing Emperor, Yishan was promoted to the emperor's bodyguard. He served in several more positions in the following decade. Yishan governed Ili from 1838 to 1840, and from 1845 to 1854. He was chosen to be a military general in 1839 for the First Opium War, and was promoted to Imperial Commissioner and Viceroy of Liangguang in 1841. Mismanagement in Guangzhou and Humen lead to his defence failures, and he was forced to sign a convention and surrender to the British. He was sentenced to death (later became imprisonment) in late 1841, but was released in 1842. In 1843, he once again became the Daoguang Emperor's bodyguard. After finishing his Ili governance term in 1854, he governed Liaoning, Heilongjiang, and Jilin as Viceroy of the Three Eastern Provinces from 1855 to 1860, signing the Treaty of Aigun with the Russian Empire regarding the Qing's northeastern borders in 1858. He participated in the Second Opium War as a general from 1857 to 1860. Yishan died on 30 June, 1878.