In mathematics, the range of a function may refer either to the codomain of the function, or the image of the function. In some cases the codomain and the image of a function are the same set; such a function is called surjective or onto. For any non-surjective function the codomain and the image are different; however, a new function can be defined with the original function's image as its codomain, where This new function is surjective.
>>>PUT SHARE BUTTONS HERE<<<
- ⭐ Core Definition: Range of a function
- Range of a function in the context of Random variable
- Range of a function in the context of Geometric transformation
- Range of a function in the context of Spectrum (physical sciences)
- Range of a function in the context of Vector-valued function
- Range of a function in the context of Codomain
- Range of a function in the context of Random variables
- Range of a function in the context of Function application
Range of a function in the context of Random variable
A random variable (also called random quantity, aleatory variable, or stochastic variable) is a mathematical formalization of a quantity or object which depends on random events. The term 'random variable' in its mathematical definition refers to neither randomness nor variability but instead is a mathematical function in which
- the domain is the set of possible outcomes in a sample space (e.g. the set which are the possible upper sides of a flipped coin heads or tails as the result from tossing a coin); and
- the range is a measurable space (e.g. corresponding to the domain above, the range might be the set if say heads mapped to -1 and mapped to 1). Typically, the range of a random variable is a subset of the real numbers.
Informally, randomness typically represents some fundamental element of chance, such as in the roll of a die; it may also represent uncertainty, such as measurement error. However, the interpretation of probability is philosophically complicated, and even in specific cases is not always straightforward. The purely mathematical analysis of random variables is independent of such interpretational difficulties, and can be based upon a rigorous axiomatic setup.
Range of a function in the context of Geometric transformation
In mathematics, a geometric transformation is any bijection of a set to itself (or to another such set) with some salient geometrical underpinning, such as preserving distances, angles, or ratios (scale). More specifically, it is a function whose domain and range are sets of points – most often a real coordinate space, or – such that the function is bijective so that its inverse exists. The study of geometry may be approached by the study of these transformations, such as in transformation geometry.
Range of a function in the context of Spectrum (physical sciences)
In the physical sciences, spectrum describes any continuous range of either frequency or wavelength values. The term initially referred to the range of observed colors as white light is dispersed through a prism — introduced to optics by Isaac Newton in the 17th century.
The concept was later expanded to other waves, such as sound waves and sea waves that also present a variety of frequencies and wavelengths (e.g., noise spectrum, sea wave spectrum). Starting from Fourier analysis, the concept of spectrum expanded to signal theory, where the signal can be graphed as a function of frequency and information can be placed in selected ranges of frequency. Presently, any quantity directly dependent on, and measurable along the range of, a continuous independent variable can be graphed along its range or spectrum. Examples are the range of electron energy in electron spectroscopy or the range of mass-to-charge ratio in mass spectrometry.
Range of a function in the context of Vector-valued function
A vector-valued function, also referred to as a vector function, is a mathematical function of one or more variables whose range is a set of multidimensional vectors or infinite-dimensional vectors. The input of a vector-valued function could be a scalar or a vector (that is, the dimension of the domain could be 1 or greater than 1); the dimension of the function's domain has no relation to the dimension of its range.
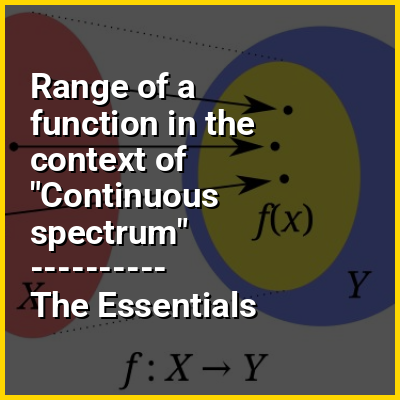
Range of a function in the context of Codomain
In mathematics, a codomain or set of destination of a function is a set into which all of the outputs of the function is constrained to fall. It is the set Y in the notation f: X → Y. The term range is sometimes ambiguously used to refer to either the codomain or the image of a function.
A codomain is part of a function f if f is defined as a triple (X, Y, G) where X is called the domain of f, Y its codomain, and G its graph. The set of all elements of the form f(x), where x ranges over the elements of the domain X, is called the image of f. The image of a function is a subset of its codomain so it might not coincide with it. Namely, a function that is not surjective has elements y in its codomain for which the equation f(x) = y does not have a solution.
Range of a function in the context of Random variables
A random variable (also called random quantity, aleatory variable, or stochastic variable) is a mathematical formalization of a quantity or object which depends on random events. The term 'random variable' in its mathematical definition refers to neither randomness nor variability but instead is a mathematical function in which
- the domain is the set of possible outcomes in a sample space (e.g. the set which are the possible upper sides of a flipped coin heads or tails as the result from tossing a coin); and
- the range is a measurable space (e.g. corresponding to the domain above, the range might be the set if say heads mapped to −1 and mapped to 1). Typically, the range of a random variable is a subset of the real numbers.
Informally, randomness typically represents some fundamental element of chance, such as in the roll of a die; it may also represent uncertainty, such as measurement error. However, the interpretation of probability is philosophically complicated, and even in specific cases is not always straightforward. The purely mathematical analysis of random variables is independent of such interpretational difficulties, and can be based upon a rigorous axiomatic setup.
Range of a function in the context of Function application
In mathematics, function application is the act of applying a function to an argument from its domain so as to obtain the corresponding value from its range. In this sense, function application can be thought of as the opposite of function abstraction.










