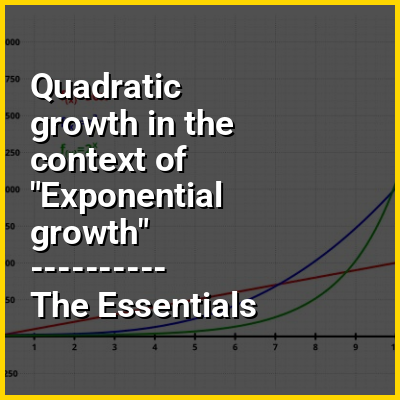
In mathematics, a function or sequence is said to exhibit quadratic growth when its values are proportional to the square of the function argument or sequence position. "Quadratic growth" often means more generally "quadratic growth in the limit", as the argument or sequence position goes to infinity – in big Theta notation, . This can be defined both continuously (for a real-valued function of a real variable) or discretely (for a sequence of real numbers, i.e., real-valued function of an integer or natural number variable).
>>>PUT SHARE BUTTONS HERE<<<
👉 Quadratic growth in the context of Exponential growth
Exponential growth occurs when a quantity grows as an exponential function of time. The quantity grows at a rate directly proportional to its present size. For example, when it is 3 times as big as it is now, it will be growing 3 times as fast as it is now.
In more technical language, its instantaneous rate of change (that is, the derivative) of a quantity with respect to an independent variable is proportional to the quantity itself. Often the independent variable is time. Described as a function, a quantity undergoing exponential growth is an exponential function of time, that is, the variable representing time is the exponent (in contrast to other types of growth, such as quadratic growth). Exponential growth is the inverse of logarithmic growth.
