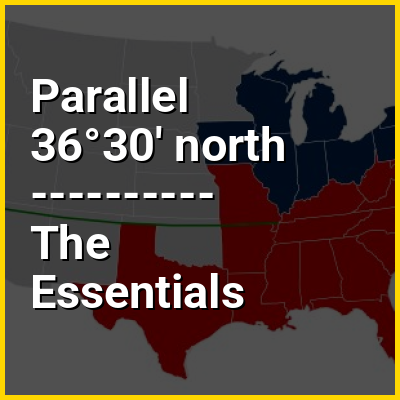
The parallel 36°30′ north (pronounced 'thirty-six degrees and thirty arcminutes') is a circle of latitude that is 36+1/2 degrees north of the equator of the Earth. This parallel of latitude is particularly significant in the history of the United States as the line of the Missouri Compromise, which was used to divide the prospective slave and free states east of the Mississippi River, with the exception of Missouri, which is mostly north of this parallel. The line continues to hold cultural, economic, and political significance to this day; the Kinder Institute for Urban Research defines the Sun Belt as being south of 36°30′N latitude.
>>>PUT SHARE BUTTONS HERE<<<
👉 Parallel 36°30′ north in the context of Sun Belt
The Sun Belt is a region of the United States generally considered stretching across the Southeast and Southwest. Another rough definition of the region is the area south of the Parallel 36°30′ north. Several climates can be found in the region—desert/semi-desert (Eastern California, Nevada, Arizona, New Mexico, Utah, and West Texas), Mediterranean (California), humid subtropical (Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Arkansas,Tennessee and Texas), and tropical (South Florida).
The Sun Belt has seen substantial population growth post-World War II from an influx of people seeking a warm and sunny climate, a surge in retiring baby boomers, and growing economic opportunities. The advent of air conditioning created more comfortable summer conditions and allowed more manufacturing and industry to locate in the Sun Belt. Since much of the construction in the Sun Belt is new or recent, housing styles and design are often modern and open. Recreational opportunities in the Sun Belt are often not tied strictly to one season, and many tourist and resort cities in the region support a tourist industry all year.
- ⭐ Core Definition: Parallel 36°30′ north
- 👉 Parallel 36°30′ north in the context of Sun Belt
- Parallel 36°30′ north in the context of Southern United States
- Parallel 36°30′ north in the context of Missouri Compromise
- Parallel 36°30′ north in the context of Texas Panhandle
- Parallel 36°30′ north in the context of Dred Scott
- Parallel 36°30′ north in the context of Presidency of James Monroe
Parallel 36°30′ north in the context of Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, Dixieland, or simply the South) is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It is between the Atlantic Ocean and the Western United States, with the Midwestern and Northeastern United States to its north and the Gulf of Mexico and Mexico to its south.
Historically, the South was defined as all states south of the 18th-century Mason–Dixon line, the Ohio River, and the 36°30′ parallel. Within the South are different subregions such as the Southeast, South Central, Upper South, and Deep South. Maryland, Delaware, Washington, D.C., and Northern Virginia have become more culturally, economically, and politically aligned in certain aspects with the Northeastern United States and are sometimes identified as part of the Northeast or Mid-Atlantic. The U.S. Census Bureau continues to define all four places as formally being in the South. To account for cultural variations across the region, some scholars have proposed definitions of the South that do not coincide neatly with state boundaries. The South does not precisely correspond to the entire geographic south of the United States, but primarily includes the south-central and southeastern states. For example, California, which is geographically in the southwestern part of the country, is not considered part of the South; however, the geographically southeastern state of Georgia is.
Parallel 36°30′ north in the context of Missouri Compromise
The Missouri Compromise (also known as the Compromise of 1820) was federal legislation of the United States that balanced the desires of northern states to prevent the expansion of slavery in the country with those of southern states to expand it. It admitted Missouri as a slave state and Maine as a free state and declared a policy of prohibiting slavery in the remaining Louisiana Purchase lands north of the 36°30′ parallel. The 16th United States Congress passed the legislation on March 3, 1820, and President James Monroe signed it on March 6, 1820.
Earlier, in February 1819, Representative James Tallmadge Jr., a Democratic-Republican (Jeffersonian Republican) from New York, had submitted two amendments to Missouri's request for statehood that included restrictions on slavery. While the slave states earlier claimed Federal protection for slavery, they now objected to any bill that imposed federal restrictions on slavery and claimed that it was a state issue, as settled by the Constitution. However, with the Senate evenly split at the opening of the debates, both sections possessing 11 states, the admission of Missouri as a slave state would give the South an advantage. Northern critics including Federalists and Democratic-Republicans objected to the expansion of slavery into the Louisiana Purchase territory on the Constitutional inequalities of the three-fifths rule, which conferred Southern representation in the federal government derived from a state's slave population.
Parallel 36°30′ north in the context of Texas Panhandle
The Texas panhandle is a region of the U.S. state of Texas consisting of the northernmost 26 counties in the state. The panhandle is a square-shaped area bordered by New Mexico to the west and Oklahoma to the north and east. It is adjacent to the Oklahoma Panhandle, land which Texas previously claimed. The 1820 Missouri Compromise declared no slavery would be allowed in states admitted from the Louisiana Purchase above 36°30′ north latitude. Texas was annexed in 1845 from still more westerly land. The Compromise of 1850 removed territory north of this line from Texas, and set the border between the Texas Panhandle and the New Mexico Territory at the 103rd meridian west. The eastern border at the 100th meridian west was inherited from the Adams–Onís Treaty of 1819, which defined the border between the United States and New Spain. The Handbook of Texas defines the southern border of Swisher County as the southern boundary of the Texas Panhandle region.
Its land area is 25,823.89 sq mi (66,883.58 km), or nearly 10% of the state's total. The Texas Panhandle is slightly larger in size than the US state of West Virginia. An additional 62.75 sq mi (162.53 km) is covered by water. Its population as of the 2010 census was 427,927 residents, or 1.7% of the state's total population. As of the 2010 census, the population density for the region was 16.6 per square mile (6.4/km). However, more than 72% of the Panhandle's residents live in the Amarillo Metropolitan Area, which is the largest and fastest-growing urban area in the region. Despite being geographically the northernmost part of Texas, the Panhandle is distinct from the region commonly called "North Texas", which is to the south and east.
Parallel 36°30′ north in the context of Dred Scott
Dred Scott (c. 1799 – September 17, 1858) was an enslaved African-American man who, along with his wife, Harriet, unsuccessfully sued for the freedom of themselves and their two daughters, Eliza and Lizzie, in the Dred Scott v. Sandford case of 1857, popularly known as the "Dred Scott decision". The Scotts claimed that they should be granted freedom because Dred had lived in Illinois and the Wisconsin Territory for four years, where slavery was illegal, and laws in those jurisdictions said that slave holders gave up their rights to slaves if they stayed for an extended period.
In a landmark case, the United States Supreme Court decided 7–2 against Scott, finding that neither he nor any other person of African ancestry could claim citizenship in the United States, and therefore Scott could not bring suit in federal court under diversity of citizenship rules. Scott's temporary residence in free territory outside Missouri did not bring about his emancipation, because the Missouri Compromise, which made that territory free by prohibiting slavery north of the 36°30′ parallel, was unconstitutional because it "deprives citizens of their [slave] property without due process of law".
Parallel 36°30′ north in the context of Presidency of James Monroe
James Monroe's tenure as the fifth president of the United States began on March 4, 1817, and ended on March 4, 1825. Monroe, a member of the Democratic-Republican Party, took office after winning the 1816 presidential election by in a landslide against Federalist Rufus King. This election was the last in which the Federalists fielded a presidential candidate, and Monroe was unopposed in the 1820 presidential election. Monroe was succeeded by his Secretary of State John Quincy Adams.
Monroe sought to eliminate political parties, and the Federalist Party faded as a national institution during his presidency. The Democratic-Republicans also stopped functioning as a unified political party, and the period during which Monroe served as president is often referred to as the "Era of Good Feelings" due to the lack of partisan conflict. Domestically, Monroe faced the Panic of 1819, the first major recession in American history. He supported many federally-funded infrastructure projects, but vetoed other projects due to constitutional concerns. Monroe signed the Missouri Compromise, which admitted Missouri as a slave state but excluded slavery in the remaining territories north of the parallel 36°30′ north.