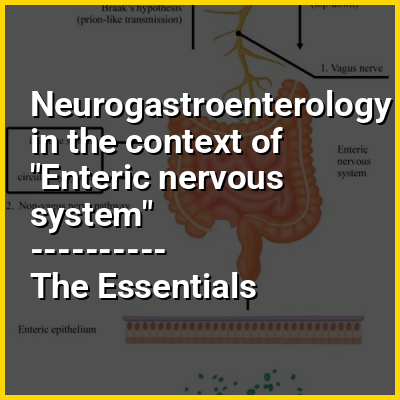
The enteric nervous system (ENS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), the others being the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS). The ENS is formed from the myenteric plexus, and the submucosal plexus, and consists of a mesh-like system of neurons that governs the functions of the gastrointestinal tract, including motility and secretion, and is known as the "second brain". It is derived from neural crest cells.
The enteric nervous system is capable of operating independently of the brain and spinal cord, but is thought to rely on innervation from the vagus nerve and prevertebral ganglia in healthy subjects. However, studies have shown that the system is operable with a severed vagus nerve. The neurons of the enteric nervous system control the motor functions of the system, in addition to the secretion of gastrointestinal enzymes. These neurons communicate through many neurotransmitters similar to the CNS, including acetylcholine, dopamine, and serotonin. The large presence of serotonin and dopamine in the intestines are key areas of research for neurogastroenterology.