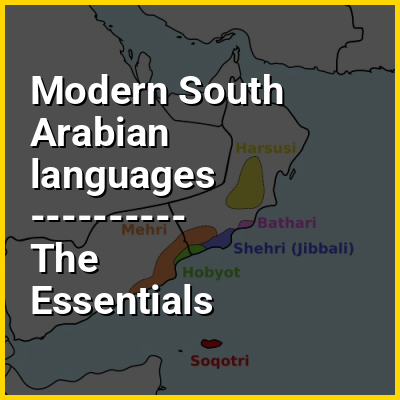
The Modern South Arabian languages, also known as Eastern South Semitic languages, are a group of endangered languages spoken by small populations inhabiting the Arabian Peninsula, in Yemen (including Socotra) and Oman. Together with the Ethiosemitic and Sayhadic languages, the Western branch, they form the South Semitic sub-branch of the Afroasiatic language family's Semitic branch.
Mehri and Hobyot are spoken in both Yemen and Oman. Soqotri is only spoken in the Yemeni archipelago of Socotra, and the Harsusi, Bathari, and Shehri languages are only spoken in Oman.