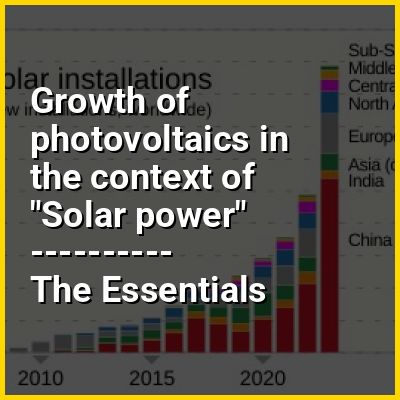
Between 1992 and 2023, the worldwide usage of photovoltaics (PV) increased exponentially. During this period, it evolved from a niche market of small-scale applications to a mainstream electricity source. From 2016 to 2022, PV has seen an annual capacity and production growth rate of around 26%, doubling approximately every three years.
When solar PV systems were first recognized as a promising renewable energy technology, subsidy programs, such as feed-in tariffs, were implemented by a number of governments in order to provide economic incentives for investments. For several years, growth was mainly driven by Japan and pioneering European countries. As a consequence, cost of solar declined significantly due to experience curve effects like improvements in technology and economies of scale. Several national programs were instrumental in increasing PV deployment, such as the Energiewende in Germany, the Million Solar Roofs project in the United States, and China's 2011 five-year-plan for energy production. Since then, deployment of photovoltaics has gained momentum on a worldwide scale, increasingly competing with conventional energy sources. In the early 21st century a market for utility-scale plants emerged to complement rooftop and other distributed applications. By 2015, some 30 countries had reached grid parity.