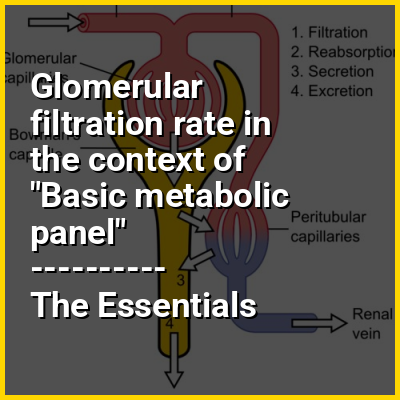
Renal functions include maintaining an acid–base balance; regulating fluid balance; regulating sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearing toxins; absorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of blood pressure; production of various hormones, such as erythropoietin; and activation of vitamin D.
The kidney has many functions, which a well-functioning kidney realizes by filtering blood in a process known as glomerular filtration. A major measure of kidney function is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR).The glomerular filtration rate is the flow rate of filtered fluid through the kidney. The creatinine clearance rate (CCr or CrCl) is the volume of blood plasma that is cleared of creatinine per unit time and is a useful measure for approximating the GFR. Creatinine clearance exceeds GFR due to creatinine secretion, which can be blocked by cimetidine. Both GFR and CCr may be accurately calculated by comparative measurements of substances in the blood and urine, or estimated by formulas using just a blood test result (eGFR and eCCr). The results of these tests are used to assess the excretory function of the kidneys. Staging of chronic kidney disease is based on categories of GFR as well as albuminuria and cause of kidney disease.