In statistics, a unit of observation is the unit described by the data that one analyzes. A study may treat groups as a unit of observation with a country as the unit of analysis, drawing conclusions on group characteristics from data collected at the national level. For example, in a study of the demand for money, the unit of observation might be chosen as the individual, with different observations (data points) for a given point in time differing as to which individual they refer to; or the unit of observation might be the country, with different observations differing only in regard to the country they refer to.
>>>PUT SHARE BUTTONS HERE<<<
👉 Data point in the context of Outlier
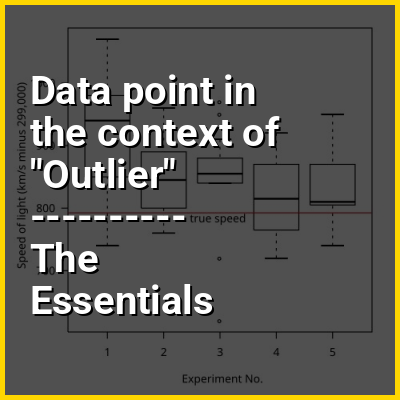
In statistics, an outlier is a data point that differs significantly from other observations. An outlier may be due to a variability in the measurement, an indication of novel data, or it may be the result of experimental error; the latter are sometimes excluded from the data set. An outlier can be an indication of exciting possibility, but can also cause serious problems in statistical analyses.
Outliers can occur by chance in any distribution, but they can indicate novel behaviour or structures in the data-set, measurement error, or that the population has a heavy-tailed distribution. In the case of measurement error, one wishes to discard them or use statistics that are robust to outliers, while in the case of heavy-tailed distributions, they indicate that the distribution has high skewness and that one should be very cautious in using tools or intuitions that assume a normal distribution. A frequent cause of outliers is a mixture of two distributions, which may be two distinct sub-populations, or may indicate 'correct trial' versus 'measurement error'; this is modeled by a mixture model.
Data point in the context of Time series
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. Examples of time series are heights of ocean tides, counts of sunspots, and the daily closing value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
A time series is very frequently plotted via a run chart (which is a temporal line chart). Time series are used in statistics, actuarial science, signal processing, pattern recognition, econometrics, mathematical finance, weather forecasting, earthquake prediction, electroencephalography, control engineering, astronomy, communications engineering, and largely in any domain of applied science and engineering which involves temporal measurements.