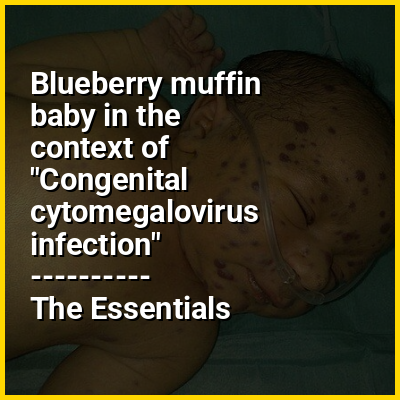
Congenital cytomegalovirus (cCMV) is cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection during pregnancy which leads the a baby being born with the infection. Most have no symptoms. Some affected babies are small. Other signs and symptoms include a rash, jaundice, hepatomegaly, retinitis, and seizures. It may lead to loss of hearing or vision, developmental disability, or a small head.
CMV is a member of the virus family herpesviridae and is the most common congenital intrauterine infection. cCMV is caused when a mother is infected with CMV in pregnancy and passes it to her unborn baby. The risk of severe disease is greatest if the mother is infected in early pregnancy; most have no symptoms. Diagnosis is by tests in the first 3-weeks after birth; on preferably urine, although saliva and blood can be used. The chance of infection is reduced by hand washing, and avoiding touching saliva or urine of very young children.