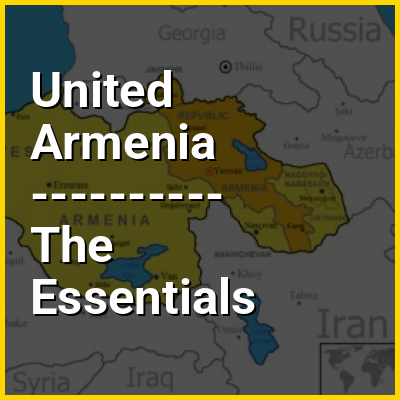
United Armenia (Armenian: Միացեալ Հայաստան, romanized: Miats'eal Hayastan), also known as Greater Armenia or Great Armenia, is an Armenian ethno-nationalist irredentist concept referring to areas within the traditional Armenian homeland—the Armenian Highlands—which are currently or have historically been mostly populated by Armenians. The idea of what Armenians see as unification of their historical lands was prevalent throughout the 20th century and has been advocated by individuals, various organizations and institutions, including the nationalist parties Armenian Revolutionary Federation (ARF or Dashnaktsutyun) and Heritage, the ASALA and others. The Republic of Armenia comprises 10%-15% of the Armenian homeland.
The ARF idea of "United Armenia" incorporates claims to Western Armenia (eastern Turkey), Nagorno-Karabakh (Artsakh), the landlocked exclave Nakhchivan (Nakhichevan) of Azerbaijan and the Javakheti (Javakhk) region of Georgia. Javakheti is overwhelmingly inhabited by Armenians. Western Armenia and Nakhchivan had significant Armenian populations until the early 20th century, and Nagorno-Karabakh until 2023, but no longer do. The Armenian population of Western Armenia was almost completely exterminated during the 1915 Armenian genocide, when the millennia-long Armenian presence in this region largely ended and Armenian cultural heritage was mainly destroyed by the Ottoman government. In 1919, the ARF-dominated government of the First Republic of Armenia declared the formal unification of Armenian lands.