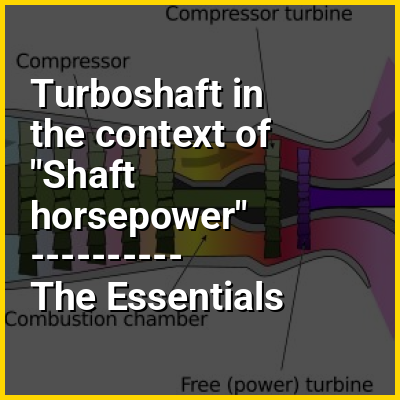
A gas turbine engine, or, informally, a gas turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the direction of flow:
- a rotating gas compressor
- a combustor
- a compressor-driving turbine.
Additional components have to be added to the gas generator to suit its application. Common to all is an air inlet but with different configurations to suit the requirements of marine use, land use or flight at speeds varying from stationary to supersonic. A propelling nozzle is added to produce thrust for flight. An extra turbine is added to drive a propeller (turboprop) or ducted fan (turbofan) to reduce fuel consumption (by increasing propulsive efficiency) at subsonic flight speeds. An extra turbine is also required to drive a helicopter rotor or land-vehicle transmission (turboshaft), marine propeller or electrical generator (power turbine). Greater thrust-to-weight ratio for flight is achieved with the addition of an afterburner.
View the full Wikipedia page for Gas turbine engine