The lead–acid battery is a type of rechargeable battery. First invented in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté, it was the first type of rechargeable battery ever created. Compared to the more modern rechargeable batteries, lead–acid batteries have relatively low energy density and heavier weight. Despite this, they are able to supply high surge currents. These features, along with their low cost, make them useful for motor vehicles in order to provide the high current required by starter motors. Lead–acid batteries suffer from relatively short cycle lifespan (usually less than 500 deep cycles) and overall lifespan (due to the double sulfation in the discharged state), as well as long charging times.
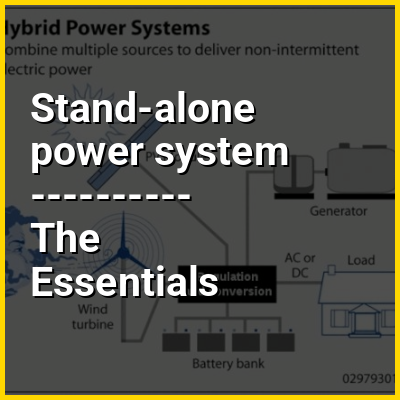
As they are not as expensive when compared to newer technologies, lead–acid batteries are widely used even when surge current is not important and other designs could provide higher energy densities. In 1999, lead–acid battery sales accounted for 40–50% of the value from batteries sold worldwide (excluding China and Russia), equivalent to a manufacturing market value of about US$15 billion. Large-format lead–acid designs are widely used for storage in backup power supplies in telecommunications networks such as for cell sites, high-availability emergency power systems as used in hospitals, and stand-alone power systems. For these roles, modified versions of the standard cell may be used to improve storage times and reduce maintenance requirements. Gel cell and absorbed glass mat batteries are common in these roles, collectively known as valve-regulated lead–acid (VRLA) batteries.