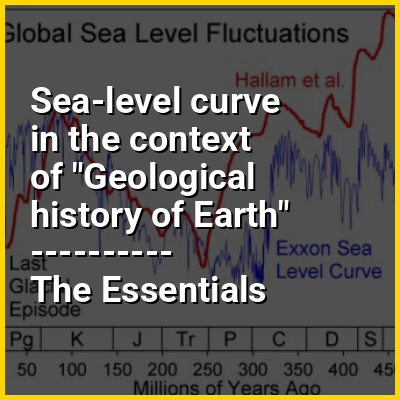
Global or barystatic sea level has fluctuated significantly over Earth's history. Over geologic time scales, the primary factors affecting sea level are the volume of available water due to growth or melting of ice caps, and the storage volume of the ocean basins due to plate tectonics. The secondary and tertiary influences on water volume are sedimentation, oceanic plume volcanism, the temperature of the seawater, which affects density, and the amounts of water retained in other reservoirs like aquifers, glaciers, lakes, and rivers. In addition to these global changes, local changes in sea level are caused by Earth's crust uplift, known as dynamic topography, and subsidence.
Over geologic timescales sea level has fluctuated by more than 100's of metres. In Archean times, most of the earth was covered by water, and early oceanic crust was relatively shallow. With time oceanic crustal composition changed, plate tectonics commenced at some point in the Proterozoic, and oceanic crust became older and deeper, creating oceans like we have currently. During the Phanerozoic, for which more geological information is available, i.e. marine fossils, sea level fluctuated by several 100's of meters, with the highest peaks generally reconstructed during the middle Paleozoic, and Cretaceous.