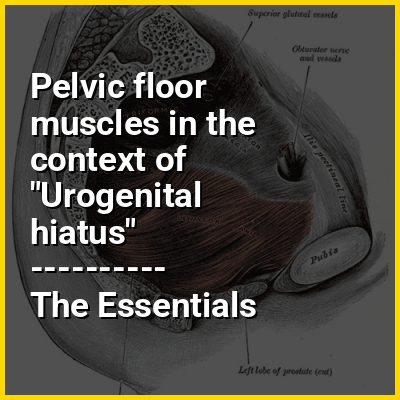
The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is an anatomical location in the human body which has an important role in urinary and anal continence, sexual function, and support of the pelvic organs. The pelvic floor includes muscles, both skeletal and smooth, ligaments, and fascia and separates between the pelvic cavity from above, and the perineum from below. It is formed by the levator ani muscle and coccygeus muscle, and associated connective tissue.
The pelvic floor has two hiatuses (gaps): (anteriorly) the urogenital hiatus through which the urethra and vagina pass, and (posteriorly) the rectal hiatus through which the anal canal passes.