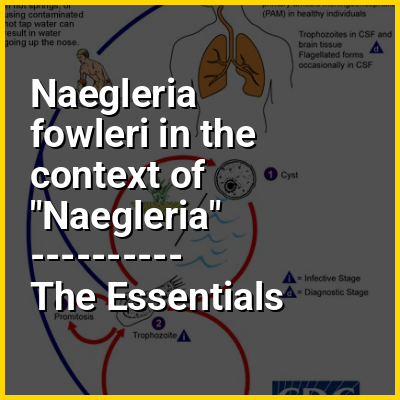
Naegleria fowleri, also known as the brain-eating amoeba, is a species of the genus Naegleria. It belongs to the phylum Percolozoa and is classified as an amoeboflagellate excavate, an organism capable of behaving as both an amoeba and a flagellate. This free-living microorganism primarily feeds on bacteria, but can become pathogenic in humans, causing an extremely rare, sudden, severe, and almost always fatal brain infection known as primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM), also known as naegleriasis.
It is typically found in warm freshwater bodies such as lakes, rivers, hot springs, warm water discharge from industrial or power plants, geothermal well water, and poorly maintained or minimally chlorinated swimming pools with residual chlorine levels under 0.5 g/m, water heaters, soil, and pipes connected to tap water. It can exist in either an amoeboid or temporary flagellate stage.