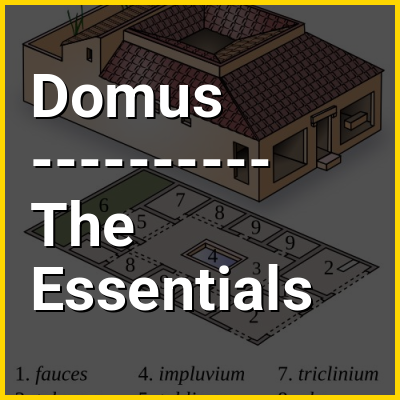
In ancient Rome, the domus (pl.: domūs, genitive: domūs or domī) was the type of town house occupied by the upper classes and some wealthy freedmen during the Republican and Imperial eras. It was found in almost all the major cities throughout the Roman territories. The modern English word domestic comes from Latin domesticus, which is derived from the word domus. Along with a domus in the city, many of the richest families of ancient Rome also owned a separate country house known as a villa. Many chose to live primarily, or even exclusively, in their villas; these homes were generally much grander in scale and on larger acres of land due to more space outside the walled and fortified city.
The elite classes of Roman society constructed their residences with elaborate marble decorations, inlaid marble paneling, door jambs and columns, as well as expensive paintings and frescoes. Many poor and lower-middle-class Romans lived in crowded, dirty and mostly rundown rental apartments, known as insulae. These multi-level apartment blocks were built as high and tightly together as possible and held far less status and convenience than the private homes of the prosperous.