In organic chemistry, diazines are a group of organic compounds having the molecular formula C4H4N2. Each contains a benzene ring in which two of the C-H fragments have been replaced by isolobal nitrogen. There are three structural isomers:
- pyridazine (1,2-diazine)
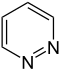
- pyrimidine (1,3-diazine)

- pyrazine (1,4-diazine)


