A cyclic compound (or ring compound) is a term for a compound in the field of chemistry in which one or more series of atoms in the compound is connected to form a ring. Rings may vary in size from three to many atoms, and include examples where all the atoms are carbon (i.e., are carbocycles), none of the atoms are carbon (inorganic cyclic compounds), or where both carbon and non-carbon atoms are present (heterocyclic compounds with rings containing both carbon and non-carbon). Depending on the ring size, the bond order of the individual links between ring atoms, and their arrangements within the rings, carbocyclic and heterocyclic compounds may be aromatic or non-aromatic; in the latter case, they may vary from being fully saturated to having varying numbers of multiple bonds between the ring atoms. Because of the tremendous diversity allowed, in combination, by the valences of common atoms and their ability to form rings, the number of possible cyclic structures, even of small size (e.g., < 17 total atoms) numbers in the many billions.
- Cyclic compound examples: All-carbon (carbocyclic) and more complex natural cyclic compounds
-
Cycloalkanes, the simplest carbocycles, including
cyclopropane,
cyclobutane,
cyclopentane, and
cyclohexane. Note, elsewhere an
organic chemistry shorthand is used where hydrogen atoms are inferred as present to fill the carbon's valence of 4 (rather than their being shown explicitly).
-
Ingenol, a complex,
terpenoid natural product, related to but simpler than the
paclitaxel that follows, which displays a complex ring structure including 3-, 5-, and 7-membered non-aromatic, carbocyclic rings.
-
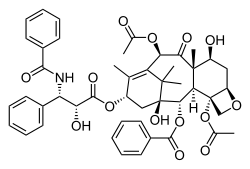
Paclitaxel, another complex, plant-derived
terpenoid, also a natural product, displaying a complex multi-ring structure including 4-, 6-, and 8-membered rings (carbocyclic and heterocyclic,
aromatic and non-aromatic).
Adding to their complexity and number, closing of atoms into rings may lock particular atoms with distinct substitution (by functional groups) such that stereochemistry and chirality of the compound results, including some manifestations that are unique to rings (e.g., configurational isomers). As well, depending on ring size, the three-dimensional shapes of particular cyclic structures – typically rings of five atoms and larger – can vary and interconvert such that conformational isomerism is displayed. Indeed, the development of this important chemical concept arose historically in reference to cyclic compounds. Finally, cyclic compounds, because of the unique shapes, reactivities, properties, and bioactivities that they engender, are the majority of all molecules involved in the biochemistry, structure, and function of living organisms, and in man-made molecules such as drugs, pesticides, etc.
View the full Wikipedia page for Cyclic compound